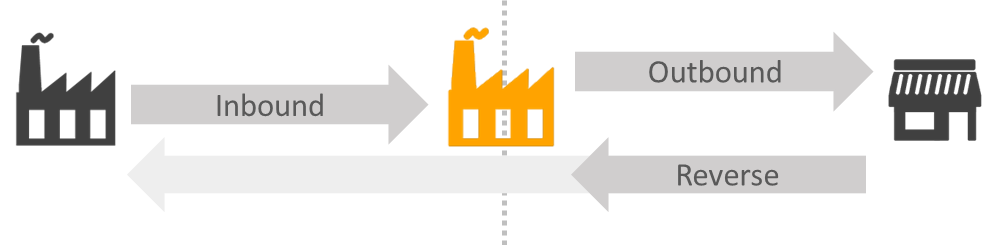
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business landscape, supply chain management plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services. While the traditional focus has been on the forward movements (inbound and outbound) of products from manufacturers to end consumers, the importance of reverse logistics is gaining recognition and in this article, we will present the concept of reverse logistics, its significance, and its impact on modern supply chain management
Defining reverse logistics
Reverse logistics is a process that deals with the efficient management of product returns, repairs, replacements, and the overall flow of materials from the customer back to the manufacturer or distributor.
It refers to the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of goods and materials in the opposite direction of the traditional supply chain. It involves activities such as product returns, recalls, repairs, refurbishments, recycling, and disposal. The goal of reverse logistics is to optimize value recapture, reduce waste, increase re-usability, and minimize the environmental impact of product returns and end-of-life disposal.
Its key components
Some of the most important activities or focuses of this specific supply chain flow are:
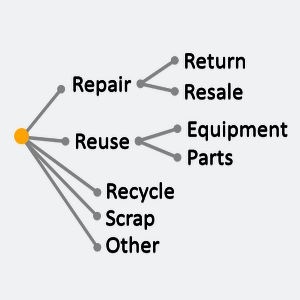
1. Product Returns Management
Reverse logistics encompasses the handling of all returned products due to customer dissatisfaction, product recalls, or warranty issues. An efficient returns management involves streamlining the reverse flow process, minimizing return shipping costs (for example using your outgoing trucks to bring back defective or end of life items from the customers), and determining appropriate disposition options for the returned items.
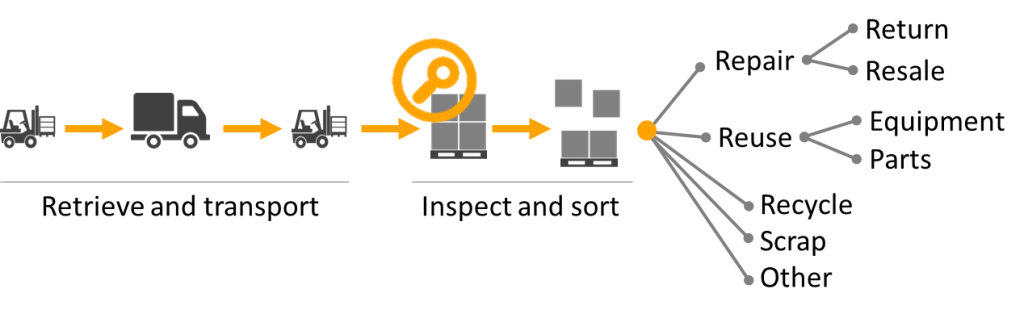
2. Repair and Refurbishment
This process includes the assessment, repair, and refurbishment of the above returned products to restore them to a saleable or usable condition. An effective repair and refurbishment processes should aim at minimizing the direct repair costs as well as the associated logistics costs and maximize the value recovered from these returned items.
3. Remanufacturing and Recycling
Reverse logistics encompasses the proper disposal and recycling of end-of-life products. This includes the extraction of valuable materials and components for reuse, reducing waste and environmental impact.
4. Transport fixtures and material re-use
This activity also relates to the re-using of transport support material such as pallets, boxes, transport fixture and similar. For example, when transporting wind turbine blades a special transport feature may have been developed or purchased by the shipper to enable the loading of 3 wind turbines onto a flatbed rather than a single one. The return of these used transport features are part of the reverse logistics chain.

5. Aftermarket Support
Reverse logistics also covers the management of spare parts, warranty services, and field service support. This ensures timely delivery of replacement parts and efficient resolution of customer issues, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Benefits of reverse Logistics
- Cost Reduction: Implementing effective reverse logistics processes can help reduce costs associated with returns management, repair, and refurbishment. It enables organizations to recapture value from returned products and salvage usable components, reducing overall waste and operational expenses.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: A well-structured reverse logistics system ensures prompt and efficient handling of product returns, repairs, and replacements. This enhances customer satisfaction, builds trust, and improves brand loyalty.
- Environmental Sustainability: this flow also plays a crucial role in minimizing waste generation and promoting sustainable practices. By implementing recycling and remanufacturing processes, organizations can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental conservation.
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Integrating reverse logistics into supply chain management optimizes the flow of materials and reduces bottlenecks. Efficient handling of returns and repairs allows organizations to quickly restock inventory and meet customer demands, leading to improved overall supply chain efficiency.
In conclusion, we can say that reverse logistics is an essential aspect of modern supply chain management, focusing on the efficient management of product returns, repairs, re-utilization, refurbishments, and end-of-life disposal. By implementing effective reverse logistics processes, organizations can reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, promote environmental sustainability, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. Recognizing the significance of this major supply chain flow and investing in its optimization can provide businesses with a competitive edge in today’s ever-evolving marketplace.
We hope you enjoyed this article and if you want to learn more about other supply chain flows – you can take a look at our article The supply chain – its material and logistics flows